85 Degrees F Is What C
tiburonesde
Nov 30, 2025 · 9 min read
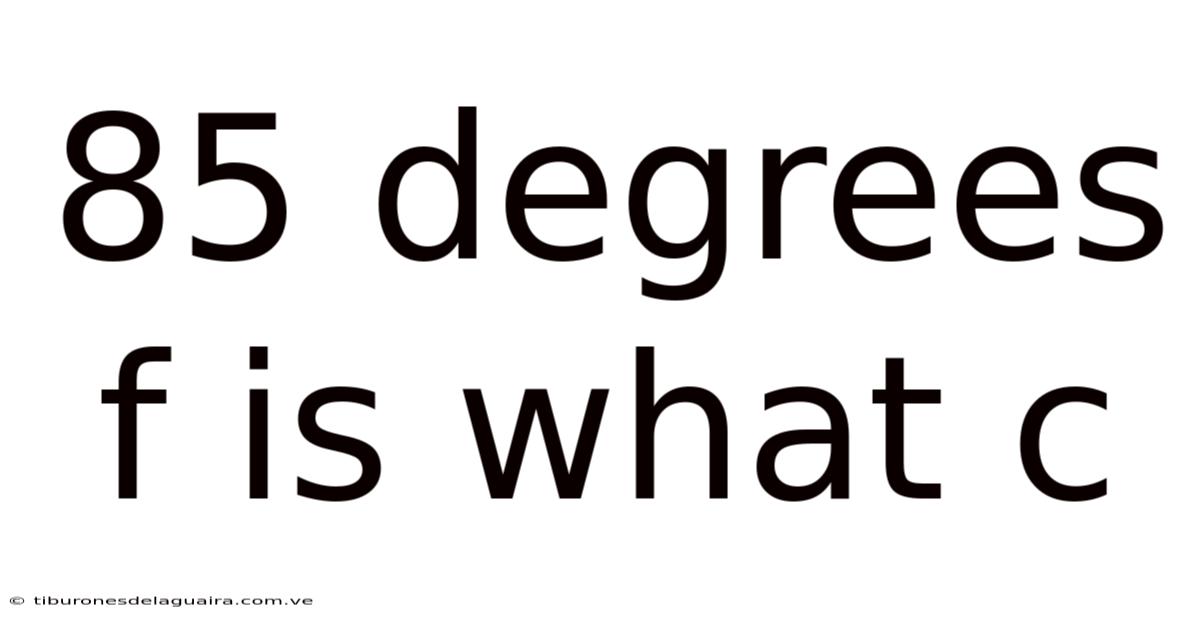
Table of Contents
The aroma of freshly baked bread and the warmth of a sunny day often bring comfort and joy. Imagine stepping out on a day where the temperature is a balmy 85 degrees Fahrenheit. You feel the gentle heat on your skin, a perfect setting for a picnic or a leisurely stroll. But have you ever wondered what that temperature translates to in Celsius, the scale used in many parts of the world?
Understanding temperature conversions is more than just a matter of curiosity; it’s a practical skill that bridges different systems of measurement. Whether you're planning a trip abroad, following an international recipe, or simply trying to make sense of a weather report from another country, knowing how to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius can be incredibly useful. So, let's explore the conversion of 85 degrees Fahrenheit into Celsius and delve into the broader context of temperature scales.
Understanding the Conversion: 85 Degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius
When we talk about 85 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius, we're essentially asking what the equivalent temperature is on a different scale. The formula to convert Fahrenheit (°F) to Celsius (°C) is:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Plugging in 85°F into the formula:
°C = (85 - 32) × 5/9 °C = 53 × 5/9 °C ≈ 29.4
Therefore, 85 degrees Fahrenheit is approximately 29.4 degrees Celsius. This conversion helps provide a clear understanding of how warm 85°F feels in a Celsius-using region.
Comprehensive Overview of Temperature Scales
To truly grasp the significance of converting 85 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius, it's essential to understand the basics of temperature scales, their origins, and their practical applications.
Fahrenheit Scale: A Historical Perspective
The Fahrenheit scale was developed in the early 18th century by German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit. He chose a scale based on two reference points: the freezing point of water mixed with salt (0°F) and the normal human body temperature (around 96°F, later refined to 98.6°F). Although not as scientifically precise as Celsius, Fahrenheit became widely adopted in the United States and a few other countries.
Celsius Scale: A Metric Standard
The Celsius scale, originally known as the centigrade scale, was created by Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius in 1742. Celsius based his scale on the freezing point of water (0°C) and the boiling point of water (100°C) at standard atmospheric pressure. This decimal-based scale aligned well with the metric system, making it easier to use in scientific and everyday applications. Today, Celsius is used in most countries around the world for weather reporting, scientific research, and general temperature measurements.
Kelvin Scale: The Absolute Standard
While Fahrenheit and Celsius are commonly used in daily life, the Kelvin scale is the standard in scientific contexts. Proposed by William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, this scale starts at absolute zero (0 K), the point at which all molecular motion ceases. Absolute zero is equivalent to -273.15°C or -459.67°F. The Kelvin scale doesn't use "degrees"; instead, temperatures are expressed in Kelvins (K). The relationship between Celsius and Kelvin is simple: K = °C + 273.15.
The Science Behind Temperature Measurement
Temperature measures the average kinetic energy of the particles within a substance. In simpler terms, it reflects how fast the atoms and molecules are moving. When we measure temperature, we're essentially quantifying this molecular motion. Different materials react differently to heat; some heat up quickly, while others require more energy to increase their temperature. This property is known as specific heat capacity.
Practical Applications of Temperature Scales
Understanding temperature scales is crucial in various fields:
- Meteorology: Weather forecasts rely on accurate temperature measurements to predict weather patterns and inform the public about expected conditions.
- Medicine: Body temperature is a vital sign used to diagnose illnesses and monitor patient health.
- Cooking: Precise temperatures are essential for baking and other culinary processes to ensure food safety and quality.
- Engineering: Temperature control is critical in many engineering applications, from designing engines to manufacturing semiconductors.
- Scientific Research: Accurate temperature measurements are fundamental to conducting experiments and analyzing data in various scientific disciplines.
Trends and Latest Developments in Temperature Measurement
The field of temperature measurement is continually evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the need for greater precision and accuracy.
Digital Thermometers
Digital thermometers have become commonplace due to their ease of use and accuracy. They use electronic sensors to measure temperature and display the reading on a digital screen. These thermometers are widely used in homes, hospitals, and industrial settings.
Infrared Thermometers
Infrared (IR) thermometers measure temperature by detecting the thermal radiation emitted by an object. They are non-contact devices, making them ideal for measuring the temperature of moving objects, hazardous materials, or surfaces that are difficult to reach.
Smart Thermostats
Smart thermostats have revolutionized home climate control by allowing users to remotely adjust temperatures and set schedules via smartphone apps. These devices often incorporate machine learning algorithms to optimize energy efficiency and provide personalized comfort.
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is playing an increasingly important role in temperature sensing. Nanoscale thermometers can measure temperature at the molecular level, offering unprecedented precision for scientific research and industrial applications.
Climate Change Monitoring
Accurate temperature data is essential for monitoring climate change and assessing its impacts on the environment. Scientists use sophisticated temperature sensors and satellite data to track global temperature trends and identify areas of concern.
Professional Insights
As technology advances, temperature measurement devices are becoming more accurate, reliable, and user-friendly. The integration of AI and machine learning is enabling smarter temperature control systems that can optimize energy usage and enhance comfort. These advancements are particularly valuable in industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation, where precise temperature control is critical.
Tips and Expert Advice on Understanding and Using Temperature Conversions
Converting between Fahrenheit and Celsius can be straightforward with the right tools and knowledge. Here are some practical tips and expert advice to help you master temperature conversions and apply them effectively in real-world scenarios.
Use Online Conversion Tools
Numerous websites and mobile apps offer instant Fahrenheit to Celsius conversion. These tools are convenient for quick conversions when you don't want to perform the calculation manually. Simply enter the temperature in Fahrenheit, and the tool will display the equivalent Celsius temperature.
For example, if you quickly need to know what 85 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius is, a simple search will instantly provide the answer of approximately 29.4°C. These tools often include additional features, such as historical temperature data and weather forecasts.
Memorize Key Reference Points
Memorizing a few key temperature reference points can help you quickly estimate conversions without needing a calculator. For example:
- 0°C = 32°F (Freezing point of water)
- 10°C = 50°F (Cool day)
- 20°C = 68°F (Room temperature)
- 30°C = 86°F (Warm day)
- 100°C = 212°F (Boiling point of water)
Knowing these reference points allows you to make educated guesses for temperatures in between. For instance, knowing that 30°C is close to 86°F makes it easier to understand that 85 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius will be slightly below 30°C.
Understand the Formula
Having a solid understanding of the conversion formula empowers you to perform manual calculations whenever needed. The formula to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius is:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
And to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit, use:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
By knowing these formulas, you can easily convert temperatures in any situation, even without access to online tools.
Consider the Context
When converting temperatures, consider the context in which the measurement is being used. In scientific or technical settings, precision is paramount, and you should use as many decimal places as necessary for accuracy. In everyday situations, rounding to the nearest whole number or tenth of a degree is usually sufficient.
Practice Regularly
The more you practice converting temperatures, the more comfortable and proficient you will become. Try converting temperatures you encounter in daily life, such as weather forecasts, recipes, and appliance settings. Regular practice will help you develop a better sense of how Fahrenheit and Celsius relate to each other.
Expert Advice
Professionals often recommend using a combination of tools and techniques for temperature conversion. Online converters are great for quick lookups, but understanding the formulas and memorizing key reference points will enhance your overall understanding. Additionally, always double-check your conversions, especially in critical applications where accuracy is essential.
FAQ About Fahrenheit to Celsius Conversion
Q: How do I convert Fahrenheit to Celsius quickly in my head?
A: A quick approximation is to subtract 30 from the Fahrenheit temperature and then halve the result. While not perfectly accurate, it provides a reasonable estimate. For 85 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius, 85 - 30 = 55, and 55 / 2 = 27.5, which is close to the actual value of 29.4°C.
Q: Why is it important to know how to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius?
A: Knowing how to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius is essential for understanding weather reports, recipes, and other temperature-related information when traveling to or communicating with people from countries that use the Celsius scale.
Q: Is there a simple way to remember the Fahrenheit to Celsius conversion formula?
A: One helpful mnemonic is "Subtract 32, multiply by 5, divide by 9." This sequence corresponds to the steps in the conversion formula: °C = (°F - 32) × 5/9.
Q: What is the difference between Fahrenheit and Celsius?
A: The Fahrenheit scale is based on the freezing point of saltwater (0°F) and human body temperature (96°F), while the Celsius scale is based on the freezing (0°C) and boiling (100°C) points of water.
Q: Can I use a smartphone app to convert temperatures?
A: Yes, numerous smartphone apps are available for converting temperatures. These apps are convenient and often offer additional features, such as unit conversions and weather information.
Conclusion
Understanding how to convert 85 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius, which is approximately 29.4°C, is more than just a technical skill; it’s a practical tool that enhances your ability to navigate different measurement systems. Whether you're planning a trip, following a recipe, or simply trying to make sense of international weather reports, knowing how to convert temperatures can be incredibly useful. By understanding the history, science, and practical applications of temperature scales, you can confidently convert temperatures and apply this knowledge in various aspects of your life.
Now that you've learned how to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius, why not put your knowledge to the test? Try converting temperatures you encounter in your daily life, or explore online resources to delve deeper into the fascinating world of temperature measurement. Engage with our content by sharing your thoughts, asking questions, or suggesting topics you'd like us to cover in future articles. Let's continue to learn and explore together!
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 85 Degrees F Is What C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.